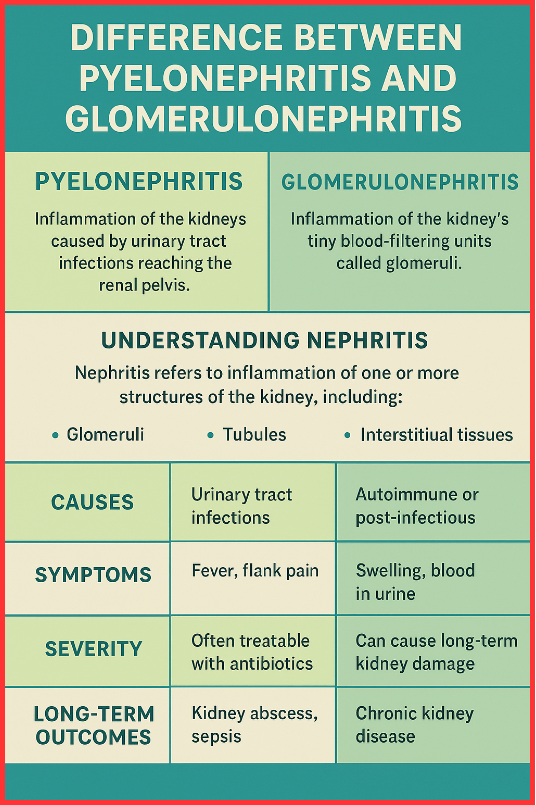
The difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis is that pyelonephritis is the inflammation of the kidneys caused by urinary tract infections reaching the renal pelvis, whereas glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the kidney’s tiny blood-filtering units called glomeruli. Both conditions fall under nephritis, but they differ in causes, symptoms, severity, and long-term outcomes.
Understanding Nephritis
Nephritis refers to inflammation of one or more structures of the kidney, including:
- Glomeruli
- Tubules
- Interstitial tissues
It may result from infections, toxins, or autoimmune disorders such as lupus. Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are two major forms of nephritis.
What is Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a kidney infection caused when bacteria from a urinary tract infection (UTI) ascend through the ureters and reach the renal pelvis.
Common Causes
- E. coli (most common bacteria)
- Sexual intercourse increasing UTI risk
- Diabetes
- Structural urinary tract abnormalities
- Spermicide use
- Blockages such as kidney stones
How the Infection Spreads
- Most often: Ascending infection from the urinary tract
- Rarely: Through the bloodstream
Symptoms of Pyelonephritis
- High fever
- Flank or back pain
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation during urination
- Nausea and vomiting
Possible Complications
- Kidney abscess
- Sepsis
- Permanent kidney damage
- Acute kidney failure (rare but severe)
Types
- Acute Pyelonephritis – sudden, severe infection
- Chronic Pyelonephritis – recurrent infections causing scarring
Diagnosis
- Urinalysis
- Urine culture
- Imaging (CT scan, ultrasound) in severe cases
Treatment
- Antibiotics such as:
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ceftriaxone
- Fluoroquinolones
- Cephalosporins
- Aminoglycosides
- Trimethoprim
Prevention Tips
- Drink plenty of water
- Urinate after intercourse
- Maintain good genital hygiene
- Cranberry juice may help reduce recurrent UTIs
Who Gets It Most?
- 1–2 per 1000 women annually
- <0.5 per 1000 men
- Young women are most affected
- Adults >65 years are at higher risk of complications
What is Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of glomeruli, the microscopic blood vessels responsible for filtering blood and producing urine.
It is more serious than typical UTIs and often linked to immune system dysfunction.
Types
- Acute Glomerulonephritis
- Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Causes of Acute Glomerulonephritis
- Post-streptococcal infection (e.g., strep throat)
- Abscessed tooth
- Autoimmune diseases:
- Lupus
- Goodpasture syndrome
- Amyloidosis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Polyarteritis nodosa
Causes of Chronic Glomerulonephritis
- Hereditary disorders
- Immune diseases
- Certain cancers
- Chemical exposure (e.g., hydrocarbon solvents)
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
- Puffy face
- Swelling in ankles and legs
- Blood in urine (tea-colored urine)
- Reduced urination
- High blood pressure
- Fluid in lungs (shortness of breath)
- Abdominal pain
- Nosebleeds
- Frequent nighttime urination
- Excess protein in urine
Diagnosis
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- Kidney imaging
- Immunological testing
- Kidney biopsy (if required)
Treatment Options
- ACE inhibitors for blood pressure
- Corticosteroids to reduce immune attack
- Plasmapheresis
- Diuretics
- Dietary changes (low salt, potassium, protein)
- Dialysis for severe cases
- Kidney transplant for end-stage damage
Similarities Between Pyelonephritis and Glomerulonephritis
Both conditions:
- Involve kidney inflammation
- Occur in both males and females
- Can be acute or chronic
- May lead to kidney failure if untreated
- Are often linked to infections
Difference Between Pyelonephritis and Glomerulonephritis (Comparison Table)
| Feature | Pyelonephritis | Glomerulonephritis |
| Definition | Infection-induced inflammation of renal pelvis | Inflammation of glomeruli (blood-filtering units) |
| Primary Cause | Bacterial UTI (mostly E. coli) | Autoimmune conditions or post-infectious response |
| Main Symptoms | Fever, flank pain, burning urination | Swelling, blood in urine, high BP |
| Spread | Ascending infection from urethra | Immune-mediated or after throat infection |
| Severity | Usually treatable with antibiotics | Can cause long-term kidney damage |
| Diagnosis | Urinalysis and urine culture | Blood tests, urine tests, biopsy |
| Treatment | Antibiotics | Steroids, ACE inhibitors, dialysis, transplant |
| Long-term Risk | Kidney abscess, sepsis | Chronic kidney disease |
Summary – Difference Between Pyelonephritis and Glomerulonephritis
The difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis lies in the part of the kidney affected and their underlying causes.
- Pyelonephritis originates from a bacterial urinary tract infection reaching the renal pelvis.
- Glomerulonephritis is an immune-related inflammation of the glomeruli, often more severe and capable of causing long-term kidney damage.
Both conditions require timely diagnosis to prevent complications such as kidney failure.
Conclusion – Pyelonephritis vs Glomerulonephritis
In conclusion, the difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis is primarily based on the infected site (renal pelvis vs. glomeruli) and the root cause (bacterial UTI vs. immune reaction). Recognizing these differences helps in choosing the right treatment and preventing permanent kidney damage. The keyword difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis remains crucial for understanding and diagnosing these kidney conditions.
Reference:
1. DiMaria, Christine. “Pyelonephritis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Pregnancy & More.” Healthline, Healthline Media.
2. “Glomerulonephritis.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
Read Next: