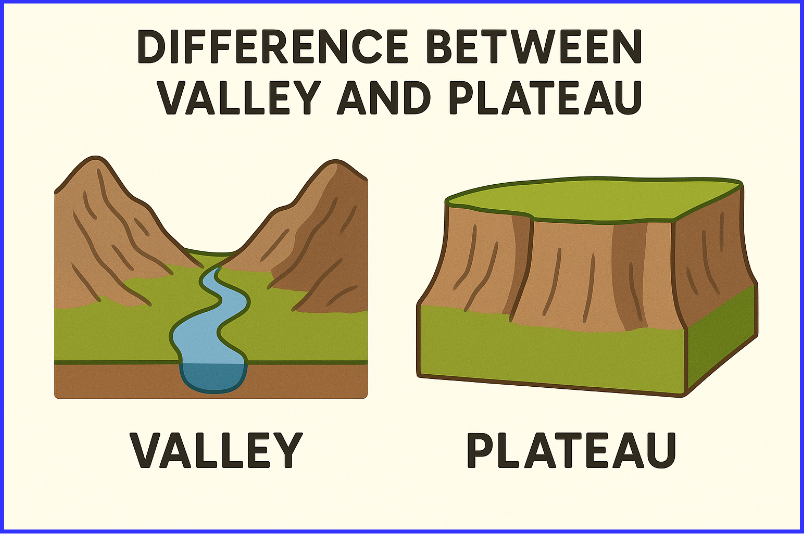
The Difference Between Valley and Plateau lies in their shape, elevation, formation, and role in the landscape. A valley is a low-lying area between hills or mountains, often with rivers flowing through it. In contrast, a plateau is an elevated flat or gently sloping landform that rises sharply above the surrounding terrain.
In short: valleys are depressions, plateaus are elevated lands. Below, we explore types, formation processes, famous examples, ecological significance, and human uses of both landforms.
What Is a Valley?
A valley is a long, narrow lowland that lies between hills or mountains. Valleys are typically formed by natural forces over millions of years. Their fertile soils and water availability often make them hubs of agriculture, settlements, and biodiversity.
Formation of Valleys
Valleys are formed mainly through three natural processes:
- River Erosion (Fluvial Valleys)
Rivers carve out valleys over millions of years. Continuous water flow erodes soil and rock, creating V-shaped valleys.- Example: Yosemite Valley, USA.
- Glacial Erosion (Glacial Valleys)
Glaciers carve deep, wide U-shaped valleys as they move downhill.- Example: Sognefjord Valley, Norway.
- Tectonic Activity (Rift Valleys)
Movement of tectonic plates creates depressions or rift valleys.- Example: Great Rift Valley, East Africa.
Types of Valleys
- V-shaped Valleys – Narrow and steep, formed by river erosion.
- U-shaped Valleys – Wide and flat, formed by glacial erosion.
- Rift Valleys – Caused by tectonic plate movements.
- Hanging Valleys – Elevated valleys formed by tributary glaciers.
Examples of Famous Valleys
- Yosemite Valley (USA) – Known for cliffs, waterfalls, and granite formations.
- Great Rift Valley (Africa) – Extends across Kenya, Tanzania, and Ethiopia.
- Loire Valley (France) – Famous for vineyards and castles.
- Kullu Valley (India) – Popular for agriculture and tourism in Himachal Pradesh.
Importance of Valleys
- Agriculture: Rich soil and water sources make valleys ideal for crops.
- Water Resources: Rivers and streams provide fresh water.
- Biodiversity: Valleys support forests, wildlife, and aquatic ecosystems.
- Settlement: Many cities and towns are built in valleys for accessibility and fertility.
What Is a Plateau?
A plateau is an elevated, flat, or gently sloping landform that stands above the surrounding terrain. Plateaus can extend over thousands of square kilometers and are often formed by volcanic activity, tectonic uplift, or erosion-resistant rock layers.
Formation of Plateaus
Plateaus form through several natural processes:
- Tectonic Uplift
Large blocks of the Earth’s crust are pushed upwards.- Example: Tibetan Plateau, the “Roof of the World.”
- Volcanic Activity
Successive lava flows create elevated flat regions.- Example: Deccan Plateau, India.
- Erosion-Resistant Rocks
Plateau surfaces resist erosion, while surrounding land is worn down.- Example: Colorado Plateau, USA.
Types of Plateaus
- Dissected Plateau – Eroded by rivers, creating valleys and cliffs.
- Volcanic Plateau – Formed by lava flows.
- Intermontane Plateau – Located between mountain ranges.
- Lava Plateau – Result of repeated lava deposits.
Examples of Famous Plateaus
- Tibetan Plateau – 4,500 meters above sea level, covers multiple Asian countries.
- Deccan Plateau (India) – Rich in minerals and fertile soils.
- Colorado Plateau (USA) – Includes Grand Canyon and Monument Valley.
- Ethiopian Highlands (Africa) – Known for fertile soils and highland culture.
Importance of Plateaus
- Agriculture: Fertile plateau regions support farming, especially terrace agriculture.
- Minerals & Mining: Many plateaus are rich in ores and minerals.
- Tourism: Scenic landscapes attract tourists.
- Climate Influence: Plateaus can affect local climate and rainfall patterns.
Similarities Between Valley and Plateau
- Both are landforms formed by natural geological processes.
- Both can host rivers, vegetation, and wildlife.
- Both influence human settlement and agriculture.
- Both evolve over time due to erosion, tectonic activity, and weathering.
Difference Between Valley and Plateau (Comparison Table)
| Aspect | Valley | Plateau |
| Definition | Low-lying land between mountains or hills. | Elevated flat or gently sloping land above surrounding terrain. |
| Elevation | Lower than surrounding land. | Higher than surrounding land. |
| Shape | Elongated, V-shaped or U-shaped. | Flat or gently sloping. |
| Formation | Formed by river, glacial erosion, or tectonic activity. | Formed by tectonic uplift, lava flows, or erosion-resistant rocks. |
| Types | V-shaped, U-shaped, rift, hanging valleys. | Dissected, volcanic, intermontane, lava plateaus. |
| Examples | Yosemite Valley, Great Rift Valley, Loire Valley, Kullu Valley. | Tibetan Plateau, Deccan Plateau, Colorado Plateau, Ethiopian Highlands. |
| Uses | Agriculture, settlements, water sources, biodiversity. | Farming, grazing, mining, tourism, climate regulation. |
Summary
The Difference Between Valley and Plateau can be summarized as:
- Valley – A depression or lowland formed by erosion or tectonic activity, often containing rivers or streams.
- Plateau – An elevated, flat or gently sloping landform formed by volcanic activity, tectonic uplift, or erosion-resistant rocks.
Valleys and plateaus are opposite in elevation, but both play vital roles in shaping the Earth’s surface and supporting ecosystems and human activities.
FAQs: Valley and Plateau
Yes. Erosion can carve valleys within a plateau, forming a dissected plateau.
A plateau is much higher than a valley, which is always a low-lying area.
Mostly, but rivers can also flow across plateaus, forming waterfalls, gorges, or lakes.
Yosemite Valley (USA), Great Rift Valley (Africa), Loire Valley (France), Kullu Valley (India).
Tibetan Plateau, Deccan Plateau (India), Colorado Plateau (USA), Ethiopian Highlands.
References:
1. “Valley.” Education – National Geographic.
2. “Plateau.” National Geographic
Read Next: