The Difference Between Nervous and Anxious is that nervous refers to a temporary feeling of stress or uneasiness before a specific situation, while anxious describes a deeper and more persistent worry that may continue even without a clear reason.
In simple words, nervous = short-term response, and anxious = ongoing mental worry.
Meaning of Nervous
Nervous is used to describe a state of temporary tension that usually appears before a particular event. It is often connected to physical symptoms like sweating, shaking, or a fast heartbeat.
A person feels nervous when they are about to face something uncertain — like an exam, interview, or performance.
Nervous – Etymology
The word nervous comes from:
- Latin: nervosus (meaning “vigorous” or “sinewy”)
- Later used to describe sensitivity of the nerves (18th century)
- Current meaning: emotionally tense or easily agitated
So, nervousness originally referred to the nerves of the body and later evolved to describe emotional tension.
Sentence Examples of Nervous
- She felt nervous before her first job interview.
- The student became nervous while waiting for the results.
- He looked nervous as he stepped onto the stage.
- The dog gets nervous during thunderstorms.
- I am a little nervous about the meeting tomorrow.
Nervous Attributes
People who feel nervous may:
- Experience temporary tension
- Have a known cause for their feeling
- Return to normal once the event passes
- Show physical signs of stress (shaky voice, sweating)
Meaning of Anxious
Anxious is used to describe a constant state of worry or fear.
Unlike nervousness, anxiety may not be connected to a specific event and can continue for days, weeks, or longer.
It affects thoughts, emotions, and sometimes daily activities.
Anxious – Etymology
The word anxious comes from:
- Latin: anxius (meaning “worried” or “troubled”)
- From angere (meaning “to choke” or “to distress”)
- Modern meaning: persistent emotional worry or fear
Sentence Examples of Anxious
- He felt anxious all week without knowing why.
- She is anxious about the future.
- The news made everyone anxious.
- He became anxious when separated from family.
- Constant pressures can make a person anxious regularly.
Anxious Attributes
People who are anxious may:
- Worry without a specific reason
- Feel prolonged emotional stress
- Struggle to relax
- Experience mental and physical discomfort (tight chest, overthinking)
Key Differences Between Nervous and Anxious
| Feature | Nervous | Anxious |
| Duration | Short-term | Long-term or recurring |
| Cause | Specific situation | May not have a clear cause |
| Nature | Temporary emotional tension | Deep emotional worry or fear |
| Physical Effect | Sweating, shaking, fast heartbeat | Restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating |
| Example | Nervous before a presentation | Anxious about life decisions |
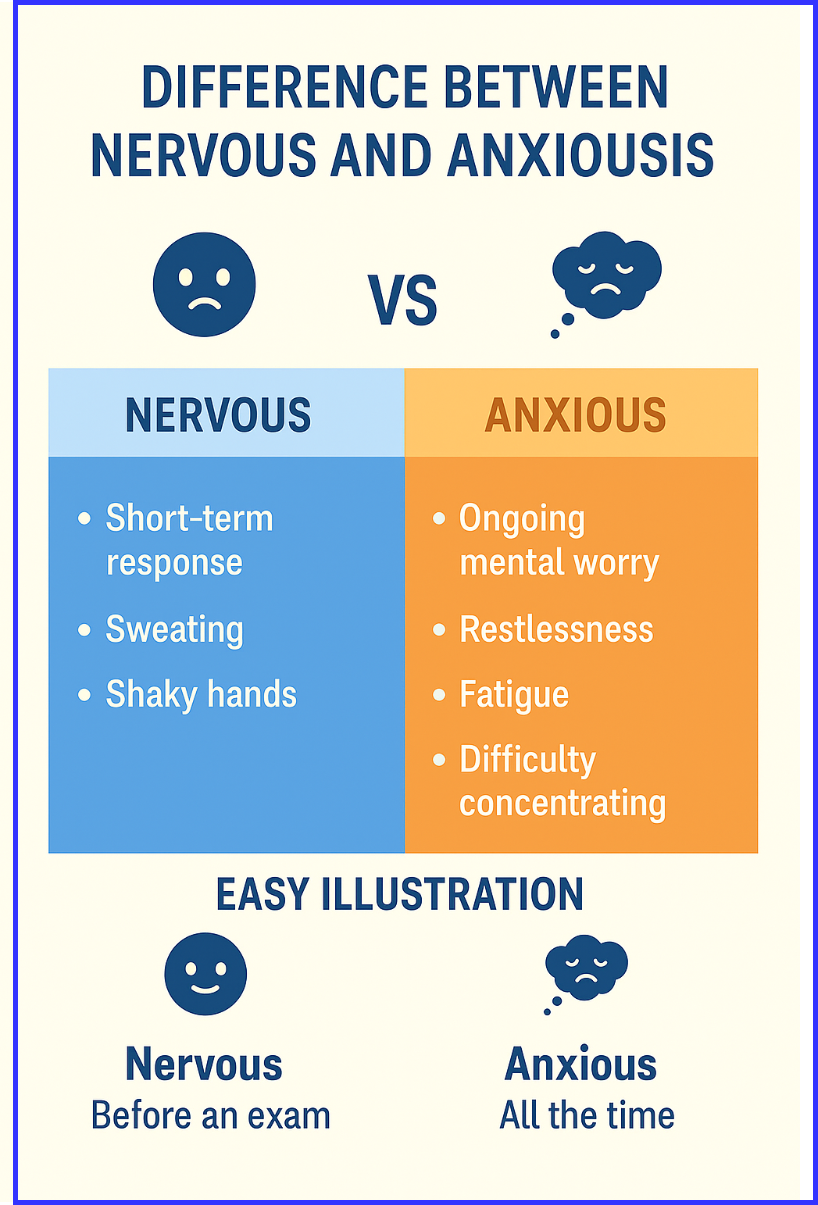
Easy Illustration to Understand the Difference
- Nervous: A student feels uneasy only before an exam, but feels fine afterward.
- Anxious: The same student keeps worrying about failure all the time, even when not preparing.
Story: Nervous vs Anxious
In a small town, two friends named Riya and Maya were preparing for a speech competition.
Riya felt nervous only on the morning of the event. Her hands shook, and her heart raced. But once she stepped on stage and started speaking, the feeling faded away. After the event, she felt perfectly fine.
Maya, however, felt anxious for many days before the competition. She could not sleep, kept imagining negative outcomes, and felt heavy in her chest even when she was not practicing. Even after the competition was over, the worry remained.
The teacher noticed the difference and explained:
Nervousness comes and goes quickly, but anxiety stays longer and affects the mind deeply.
Conclusion
Understanding the Difference Between Nervous and Anxious helps us express feelings more accurately.
While nervousness is a temporary and normal reaction to a particular situation, anxiety is deeper and long-lasting, sometimes needing emotional support or professional help. Recognizing this distinction promotes better self-awareness, communication, and mental well-being.
Reference:
1. Jones, Heather. “Nervousness.” Very Well Health.
2. “Anxiety.” Medline Plus.
Read Next: