The difference between apheresis and dialysis is that apheresis removes a specific component of the blood and returns the rest, while dialysis removes waste products and excess fluid when the kidneys fail to work properly. Both are extracorporeal treatments but serve entirely different medical purposes.
To understand the difference between apheresis and dialysis, it’s important to know how each procedure works, when it is used, and what part of the blood it targets. Although both processes clean or filter the blood outside the body, they are used for very different health conditions.
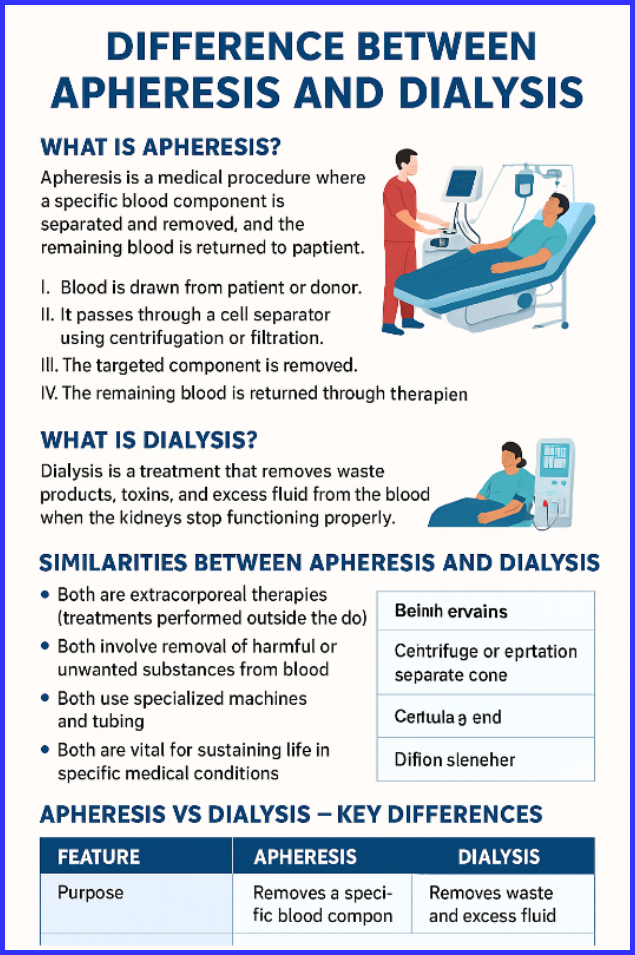
What is Apheresis?
Apheresis is a medical procedure where a specific blood component is separated and removed, and the remaining blood is returned to the patient.
It is also known as hemapheresis.
How Apheresis Works
- Blood is drawn from the patient or donor.
- It passes through a cell separator using centrifugation or filtration.
- The targeted component is removed.
- The remaining blood is returned through another line.
Common Types of Apheresis (With Examples)
- Plasmapheresis: Removal of plasma.
Used in autoimmune disorders like Guillain-Barré syndrome. - Leukapheresis: Removal of white blood cells.
Used in leukemia patients with very high WBC counts. - Plateletpheresis: Removal of platelets.
Used for platelet donations. - Granulocytapheresis: Removal of granulocytes.
- Lymphocytapheresis: Removal of lymphocytes.
When is Apheresis Used?
- During blood donation (e.g., platelet donation).
- For treating diseases caused by abnormal blood components (e.g., plasma disorders).
- To remove harmful antibodies in autoimmune diseases.
What is Dialysis?
Dialysis is a treatment that removes waste products, toxins, and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys stop functioning properly.
Why Dialysis is Needed
Healthy kidneys filter out urea, creatinine, and extra water from the blood.
Conditions like chronic kidney disease (CKD) or acute kidney injury (AKI) reduce kidney function, leading to toxin buildup. Dialysis takes over this filtering process.
Types of Dialysis (With Examples)
1. Hemodialysis
- Blood is pumped into an external dialysis machine.
- The machine removes waste and excess water.
- Clean blood is returned to the body.
Usually performed at dialysis centers.
2. Peritoneal Dialysis
- Uses the peritoneum (abdominal lining) as a natural filter.
- A special dialysis fluid is infused into the abdomen.
- Waste products pass from the blood into this fluid, which is later drained.
Can be performed at home (CAPD or APD).
Similarities Between Apheresis and Dialysis
- Both are extracorporeal therapies (treatments performed outside the body).
- Both involve removal of harmful or unwanted substances from blood.
- Both use specialized machines and tubing.
- Both are vital for sustaining life in specific medical conditions.
Apheresis vs Dialysis – Key Differences (Tabular Comparison)
| Feature | Apheresis | Dialysis |
| Purpose | Removes a specific blood component | Removes waste and excess fluid |
| Used For | Abnormal cells, antibodies, or plasma | Kidney failure |
| Blood Components Targeted | Plasma, platelets, WBCs, etc. | Waste products, electrolytes, fluid |
| Replacement Needed? | Sometimes (e.g., plasma replaced) | Not needed |
| Frequency | Depending on condition, often short-term | Regularly (3–4 times/week for CKD) |
| Performed On | Donors & patients | Mainly kidney disease patients |
| Method | Centrifuge or filtration separates components | Diffusion and ultrafiltration clean blood |
Summary – Difference Between Apheresis and Dialysis
The difference between apheresis and dialysis lies in their purpose and function. Apheresis removes a specific blood component, such as plasma or platelets, and returns the rest of the blood to the patient. Dialysis cleanses the blood by removing waste products and excess fluid when the kidneys fail to perform their role. Both therapies are life-saving but serve different clinical needs.
Reference:
1. “Apheresis.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
2. “Dialysis.” NHS Choices, NHS.
Read Next: