The Difference Between Junctional and Idioventricular Rhythm lies in their site of origin, heart rate, ECG appearance, and clinical significance, with junctional rhythms arising from the AV junction and idioventricular rhythms originating from the ventricles.
Understanding this distinction is critical for clinicians, students, and anyone interpreting ECGs, as confusing these rhythms can lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate management. This article provides a detailed comparison of junctional rhythm vs idioventricular rhythm, ECG characteristics, identification tips, and clinical relevance.
Overview of Cardiac Escape Rhythms
Escape rhythms occur when the primary pacemaker (SA node) fails or conduction is blocked. Secondary pacemakers then take over to maintain cardiac output. These include:
- Junctional escape rhythms
- Idioventricular (ventricular escape) rhythms
Understanding junctional vs idioventricular rhythm requires knowing where the impulse originates and how it appears on ECG.
What Is Junctional Rhythm?
A junctional rhythm originates from the atrioventricular (AV) junction, typically when the SA node fails or impulses cannot reach the ventricles.
Key Features of Junctional Rhythm
- Origin: AV node or AV junction
- Rate: 40–60 bpm
- QRS: Narrow (<120 ms)
- P waves:
- Absent
- Inverted
- Or appear after the QRS
This rhythm is usually more stable than ventricular rhythms.
What Is Idioventricular Rhythm?
Idioventricular rhythm (IVR) arises from the ventricular myocardium and is a protective escape rhythm when higher pacemakers fail.
Key Features of Idioventricular Rhythm
- Origin: Ventricles
- Rate: 20–40 bpm
- QRS: Wide (>120 ms)
- P waves: Absent or dissociated
- Rhythm: Regular
Idioventricular rhythm is often seen in severe conduction system failure.
Difference Between Junctional and Idioventricular Rhythm
This table summarizes the Difference Between Junctional and Idioventricular Rhythm clearly for quick reference.
| Feature | Junctional Rhythm | Idioventricular Rhythm |
| Origin | AV junction | Ventricles |
| Rate | 40–60 bpm | 20–40 bpm |
| QRS Width | Narrow | Wide |
| P Waves | Absent / inverted | Absent |
| Stability | Relatively stable | Less stable |
| Clinical Risk | Moderate | Higher |
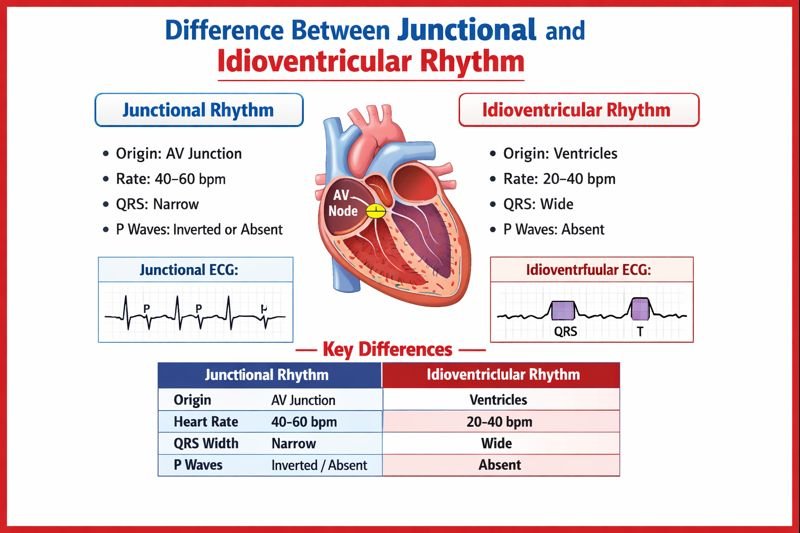
Idioventricular Rhythm ECG vs Junctional ECG
Junctional ECG Characteristics:
- Narrow QRS complexes
- Inverted P waves in II, III, aVF
- P waves may follow QRS
Idioventricular Rhythm ECG Characteristics:
- Wide, bizarre QRS complexes
- No consistent P waves
- AV dissociation may be present
When comparing idioventricular vs junctional ECG, QRS width is the most reliable differentiator.
How to Identify Idioventricular Rhythm
To correctly identify IVR on ECG, follow these steps:
- Assess heart rate – usually 20–40 bpm
- Look at QRS width – wide (>120 ms)
- Check for P waves – absent or dissociated
- Assess rhythm regularity – typically regular
Knowing how to identify idioventricular rhythm helps avoid confusing it with ventricular tachycardia or PVCs.
Idioventricular Rhythm vs Junctional Escape
| Feature | Junctional Escape | Idioventricular Escape |
| Rate | 40–60 bpm | 20–40 bpm |
| QRS | Narrow | Wide |
| Origin | AV node | Ventricles |
| Prognosis | Better | Poorer |
Idioventricular rhythm vs junctional escape mainly differs in rate and QRS morphology.
Idioventricular Rhythm vs Ventricular Escape
These terms are often used interchangeably.
- Idioventricular rhythm is a type of ventricular escape rhythm
- Ventricular escape rhythms include:
- Idioventricular rhythm
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
Thus, idioventricular rhythm vs ventricular escape is more of a semantic distinction than a functional one.
Junctional vs Ventricular Escape Rhythm
| Aspect | Junctional Escape | Ventricular Escape |
| Pacemaker | AV junction | Ventricles |
| QRS | Narrow | Wide |
| Rate | Faster | Slower |
| Hemodynamics | Better | Worse |
Understanding junctional vs ventricular escape rhythm is crucial in bradycardia management.
Ventricular Escape Rhythm vs PVC
| Feature | Ventricular Escape | PVC |
| Timing | Late | Early |
| Function | Protective | Ectopic |
| Rhythm | Regular | Irregular |
| Clinical Role | Life-saving | Often benign |
This distinction helps avoid mistaking escape rhythms for ectopy.
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm vs Junctional
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (AIVR) has a faster ventricular rate.
| Feature | AIVR | Junctional Rhythm |
| Rate | 40–100 bpm | 40–60 bpm |
| QRS | Wide | Narrow |
| Seen In | Reperfusion, MI | SA node failure |
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm vs junctional differentiation relies heavily on QRS width.
Accelerated Junctional vs Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
| Feature | Accelerated Junctional | Accelerated Idioventricular |
| Origin | AV junction | Ventricles |
| QRS | Narrow | Wide |
| Rate | 60–100 bpm | 40–100 bpm |
Both are faster escape rhythms but have distinct ECG features.
IVR vs Junctional: Key Diagnostic Clues
When deciding IVR vs junctional, remember:
- Wide QRS = ventricular
- Narrow QRS = junctional
- Very slow rate favors IVR
Clinical Significance and Management
Junctional Rhythm:
- Often well tolerated
- Treat underlying cause
- Rarely needs pacing
Idioventricular Rhythm:
- Indicates severe conduction disease
- May cause hypotension
- Often requires pacing or intervention
Common Mistakes in ECG Interpretation
- Confusing IVR with ventricular tachycardia
- Mistaking PVCs for escape rhythms
- Ignoring QRS width
Correct identification of idioventricular vs junctional rhythm prevents inappropriate treatment.
Summary Table
| Parameter | Junctional Rhythm | Idioventricular Rhythm |
| Origin | AV junction | Ventricles |
| Rate | 40–60 bpm | 20–40 bpm |
| QRS | Narrow | Wide |
| Stability | Higher | Lower |
| Clinical Risk | Moderate | High |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Difference Between Junctional and Idioventricular Rhythm is based on the site of impulse generation, ECG morphology, heart rate, and clinical implications. Junctional rhythms arise from the AV junction with narrow QRS complexes and moderate rates, while idioventricular rhythms originate in the ventricles with wide QRS complexes and slower rates.
Accurate differentiation between junctional vs idioventricular rhythm, idioventricular rhythm ECG vs junctional, and related comparisons is essential for safe ECG interpretation and patient management.
Reference:
1. Gangwani, Manesh Kumar. “Idioventricular Rhythm.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 7 Apr. 2021.
2. Hafeez, Yamama. “Junctional Rhythm.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 19 July 2021.
Read Next:
- Difference Between Pyelonephritis and Glomerulonephritis
- Difference Between Chemotaxis and Diapedesis
- Difference Between Isosmotic Hyperosmotic and Hypoosmotic
- Difference Between Male and Female Sternum
- Difference Between Paresthesia and Dysesthesia
- Difference Between Dextrose, Dextrin, and Dextran
- Difference Between Hemolysis and Crenation