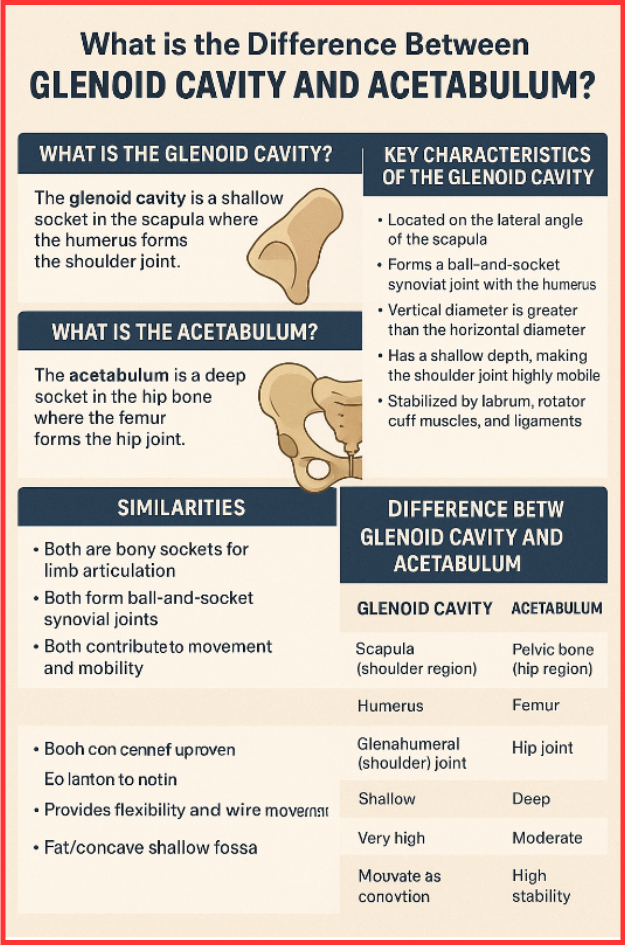
The difference between glenoid cavity and acetabulum lies mainly in their location and function. The glenoid cavity is a shallow socket in the scapula where the humerus forms the shoulder joint, while the acetabulum is a deep socket in the hip bone where the femur forms the hip joint. This difference affects their mobility, structure, and weight-bearing abilities.
Understanding the difference between glenoid cavity and acetabulum is essential for students of anatomy, physiotherapy, and medical sciences. Both are bony sockets that anchor limbs to the axial skeleton, but they differ significantly in their structure, movement, stability, and location. These cavities help form two of the most important joints—the shoulder and the hip.
What is the Glenoid Cavity?
The glenoid cavity, also called the glenoid fossa, is a shallow, pear-shaped depression on the scapula. The head of the humerus fits into this cavity to form the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint.
Key Characteristics of the Glenoid Cavity
- Located on the lateral angle of the scapula
- Forms a ball-and-socket synovial joint with the humerus
- Vertical diameter is greater than the horizontal diameter
- Has a shallow depth, making the shoulder joint highly mobile
- Stabilized by labrum, rotator cuff muscles, and ligaments
Function of the Glenoid Cavity
The shallow design allows the shoulder joint to move with exceptional freedom. It provides:
- Largest range of motion in the body
- Flexion up to 120° unsupported
- Rotation, abduction, adduction, and circumduction
Example
A simple example of the glenoid cavity in action is the movement of the arm while painting a wall or throwing a ball.
What is the Acetabulum?
The acetabulum is a large, cup-shaped cavity of the pelvic bone, formed by the fusion of the ilium, ischium, and pubis. The head of the femur fits into this cavity to create the hip joint.
Key Characteristics of the Acetabulum
- Deep, cup-like socket
- Located in the pelvis
- Forms a strong ball-and-socket synovial joint
- Surrounding bones fuse during development to form the acetabular surface
- Provides high stability for body weight support
Function of the Acetabulum
Its primary function is weight-bearing and mobility by supporting:
- Standing
- Walking
- Running
- Jumping
- Climbing
Example
When you climb stairs or run, the acetabulum bears your body weight efficiently while permitting smooth movement.
Similarities Between Glenoid Cavity and Acetabulum
Both cavities share several common features:
- Both are bony sockets for limb articulation
- Both form ball-and-socket synovial joints
- Both contribute to movement and mobility
- Issues in either cavity may lead to joint disorders such as arthritis or dislocation
Difference Between Glenoid Cavity and Acetabulum (Tabular Comparison)
| Feature | Glenoid Cavity | Acetabulum |
| Location | Scapula (shoulder region) | Pelvic bone (hip region) |
| Connected Bone | Humerus | Femur |
| Joint Formed | Glenohumeral (shoulder) joint | Hip joint |
| Depth | Shallow | Deep |
| Mobility | Very high | Moderate |
| Stability | Low (more prone to dislocation) | High (strong stability) |
| Function | Provides flexibility and wide movement | Supports body weight and enables locomotion |
| Type of Socket | Flat/concave shallow fossa | Cup-shaped deep cavity |
Summary – Glenoid Cavity vs Acetabulum
In summary, the difference between glenoid cavity and acetabulum is primarily based on their structure and function. The glenoid cavity is a shallow shoulder socket designed for flexibility and wide movement, while the acetabulum is a deep hip socket built for weight-bearing and stability. Both play crucial roles in connecting limbs to the axial skeleton.
Conclusion
The major difference between glenoid cavity and acetabulum is that the glenoid cavity supports upper-limb mobility, whereas the acetabulum supports lower-limb stability and weight. Understanding these differences is essential for studying human anatomy, orthopedics, and biomechanics.
Reference:
1. “Glenoid Cavity.”An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
2. “Acetabulum Fractures.” Boston Medical Center.
Read Next: